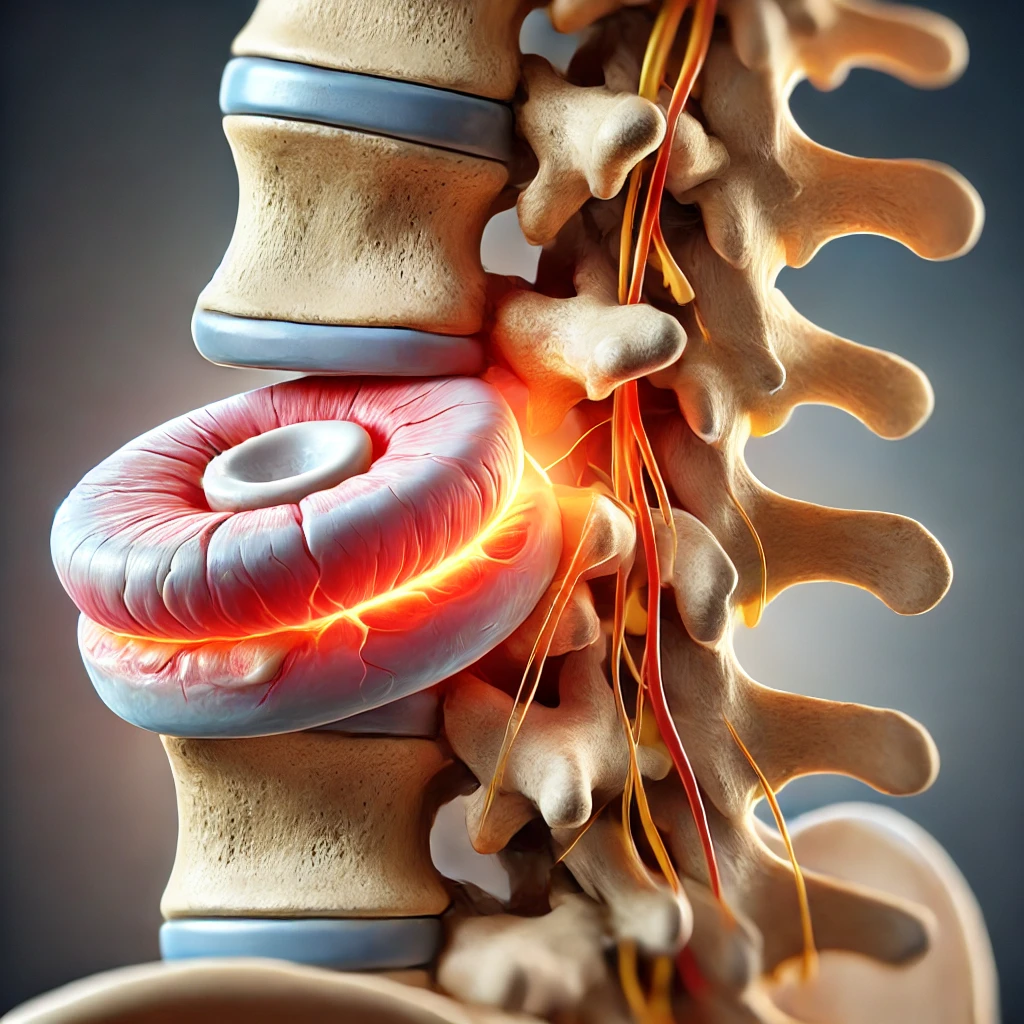
Disc herniation, also known as intervertebral disc herniation, is a condition that occurs when the soft tissue of an intervertebral disc, which acts as a cushion between the vertebrae of the spine, bulges out of its normal position. This condition can lead to pain, weakness, and some neurological issues, depending on the location of the herniation and the pressure on the nerves. This discussion aims to explore disc herniation, including its symptoms, causes, reactions, and treatments, to raise awareness and provide better support for those affected.
Symptoms
The symptoms of disc herniation can vary depending on the location of the herniation and the degree of pressure on the nerves. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Lower Back Pain: Often, there is intense pain in the lower back that may increase with bending or lifting heavy objects.
Radicular Pain: Pain may radiate down the leg (sciatica), depending on which nerve is affected.
Weakness and Numbness: Weakness and numbness may occur in the extremities, indicating nerve compression.
Bowel or Bladder Control Issues: In severe cases, disc herniation can lead to problems with controlling these functions.
Causes
The causes of disc herniation can vary, but some of the most common include:
Disc Degeneration: With age, the discs in the spine lose elasticity and strength, increasing the likelihood of herniation.
Trauma: Injury to the spine, especially from acute injuries, can lead to herniation.
Genetic Factors: A family history of disc herniation may increase the risk of developing this condition.
Unhealthy Lifestyle Choices: Obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor posture can contribute to disc injury.
Reactions
Reactions to disc herniation often vary based on the severity of symptoms and individual circumstances. Some individuals may feel frustrated and anxious due to limitations in their activities. Others may develop stress and anxiety because of chronic pain and uncertainty about treatment and recovery. It is crucial to pay attention to mental health and emotional support during this process.
Treatments
Treatments for disc herniation can include:
Conservative Therapy: Physical therapy, specific exercises, and pain management methods, such as anti-inflammatory medications and analgesics, can help control symptoms.
Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation and pain in the affected area.
Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the herniated disc or decompress the affected nerves.
Lifestyle Adaptations: Changes in diet, increased physical activity, and exercises to strengthen the muscles around the spine can be beneficial in preventing further issues.
Disc herniation is a condition that can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and possible treatments is essential for managing this condition. Early detection and appropriate management can help improve function and reduce pain, allowing individuals to lead active and fulfilling lives. It is important to consult with a medical professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.